Introduction: The Discount Trap in Retention
Discounting is an instinctive move when retention becomes a challenge. When customer churn rises or repeat rates fall, offering “20% off your next order” seems like a quick win. But while discounts might temporarily lift transactions, they do not solve the core problem of weak customer relationships.
In reality, discounts often mask deeper engagement issues. The hidden costs are substantial:
- Margin erosion eats into profitability.
- Customers become deal-seekers, commoditizing your offering.
- Loyalty becomes fragile: customers stick around only until a better deal appears elsewhere.
Retention rooted in discounts is retention built on sand. Sustainable retention demands a better approach: building emotional equity and delivering experiences that make customers want to stay — not just transact.
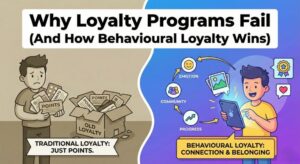
Rethinking Retention: Loyalty Built on Behavior
Loyalty is frequently misunderstood as a transactional metric: spend more, stay longer. But true loyalty goes deeper — it is about emotional equity, not price elasticity.
Behavior-based loyalty means understanding what your customer values and designing engagements that reinforce those values. This could mean helping them discover new benefits of your product, recognizing key milestones in their journey, or simply being relevant when they need you most.
Retention should be a reflection of how well you understand your customer’s context — their needs, habits, and preferences. When you build this understanding, stickiness happens organically. Customers return because they value the relationship, not because they’re waiting for another coupon.
Behavioral Insight as the Foundation
A retention strategy that moves beyond discounts must be grounded in behavioral insight.
Collecting Behavioral Signals Beyond Purchases
Purchases are just the tip of the iceberg. The richer picture emerges from signals like:
- Browse depth: How far do users go when exploring your catalog?
- Repeat visits: How often do they return even if they don’t buy?
- Feature adoption: What parts of your service or product are they using most?
These signals give you context on interest, intent, and friction points.
The Value of Passive and Active Engagement Signals
It’s important to capture both passive behaviors (scroll depth, session duration) and active behaviors (wishlist additions, referrals). Together, these reveal where customers are leaning in and where they might be slipping away.
Segmenting Users by Behavioral Profiles
Many brands still segment by traditional methods — high spenders vs low spenders, or frequency of purchase. A modern approach layers behavioral profiling: segmenting by exploration patterns, engagement preferences, and lifecycle stage.
This enables tailored interventions that resonate with what customers are actually doing, not just what they’ve bought.
Personalized Journeys: Experiences that Matter
Generic lifecycle campaigns — welcome emails, monthly newsletters, blanket winback offers — no longer cut it. Personalization is the linchpin of non-discount retention.
From One-Size-Fits-All to Individualized Communication
Every customer journey is different. Personalization means adapting communications and touchpoints based on:
- Where they are in the lifecycle
- Their historical engagement
- Predictive signals of their intent or disengagement
Behavior-Led Lifecycle Journeys
Examples include:
- Onboarding: Educating a new customer on product benefits based on what they browsed pre-purchase.
- Milestone engagement: Recognizing when a customer completes their first three purchases — without resorting to discounts.
- Early drop-off rescue: Intervening when a customer shows declining engagement patterns, e.g., fewer app opens or shorter session times.
Avoiding Excessive Nudges
Critical to this approach is respecting the customer’s attention. Excessive notifications or irrelevant nudges backfire and accelerate churn. Smart personalization ensures communications are timely, valuable, and never intrusive.
Measuring Retention Health Without Relying on Discounts
A behavior-led retention strategy also needs better measurement frameworks.
RFM, Cohort Analysis, and Propensity Models
Key analytical tools:
- RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) analysis: Understand value and engagement recency.
- Cohort analysis: Identify how behavior and retention vary by acquisition cohort.
- Churn propensity models: Predict who is at risk before churn happens.
Engagement Metrics as Leading Indicators
Retention is often measured retrospectively — did they return, did they purchase? A smarter approach uses engagement metrics as leading indicators:
- Declining session durations
- Reduced interaction with key features
- Fewer responses to past communications
These offer an early warning system for intervention before churn becomes visible.
Feedback Loops
Qualitative feedback complements behavioral insight:
- In-app surveys
- Exit interviews
- Periodic NPS pulses
This gives context to quantitative signals and surfaces “why” behind disengagement.
Case Studies & Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a D2C wellness brand that saw rising churn after the first order. Instead of offering repeat-purchase discounts, they analyzed post-purchase behavior:
- Insight: Customers weren’t using key features that would help integrate the product into their routines.
- Action: They launched behavior-led onboarding journeys personalized to product type, helping customers establish early habits.
- Result: Retention rose by 18% without discount incentives.
In the OTT space, platforms have successfully mitigated silent churn — customers who stop watching but don’t cancel — by identifying behavioral drop-offs (e.g., decreasing watch duration) and intervening with tailored recommendations, not discounts.
These examples illustrate that retention is a function of understanding and responding to behavior, not bribing users to stay.
Building Internal Capability for Non-Discount Retention
Executing this kind of strategy requires teams and tools purpose-built for behavioral insight.
Teams and Tooling
- CRM platforms: To orchestrate personalized journeys.
- Analytics capability: To track and interpret behavioral signals.
- Experimentation frameworks: To test and learn what drives engagement.
Tech-Agnostic Strategy
Importantly, the strategy matters more than the stack. Whether you use Clevertap, WebEngage, Braze, or something else — behavioral retention depends on how you use the tools, not the tools themselves.
Conclusion: From Transaction to Relationship
Retention without discounts is not just a viable strategy — it’s a sustainable one. It protects margins, builds stronger relationships, and insulates your brand from commoditization.
If your current retention strategy is dominated by discount offers, it’s time for a reset. Audit your retention levers:
- What behavioral signals are you tracking?
- Are you personalizing based on behavior or relying on static journeys?
- How early can you detect disengagement?
Retention success starts when you treat every customer as more than just a potential transaction — and when you build journeys that respect their behavior, preferences, and context.